What is Chronic Back Pain?
Backache
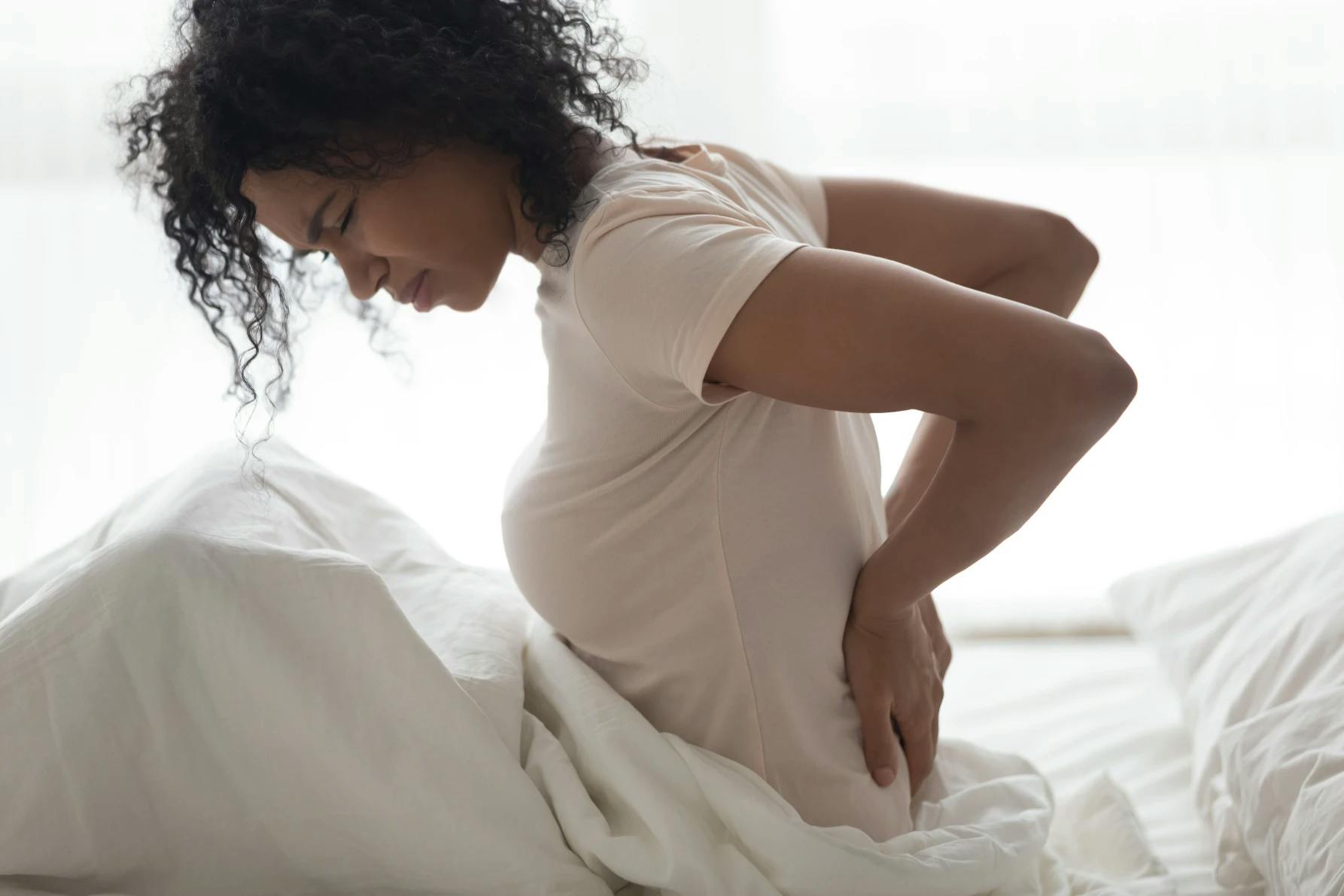
Most people will experience bouts of back pain in their lives: it’s one of the most common health issues that affects those of all ages. Chronic back pain, on the other hand, lasts for more than 12 weeks and becomes a persistent condition, interfering both with daily activities as well as work schedules.
Chronic back pain is commonly felt as muscle aches, and a shooting, burning or stabbing sensation.1 The pain can be concentrated along the spine, in the lower back, and radiating down either leg and below the knee. Bending, twisting or moving one’s core can exacerbate this pain.
Chronic back pain can be caused by several factors, including:
- Injuries or accidents
- Poor posture
- Obesity
- Arthritis
- Herniated or slipped disc
While chronic back pain can be frustrating and debilitating, it is not a life-threatening condition. However, it can impact a person's quality of life and require proper management. In some cases, immediate medical care may be required—such as in combination with bowel issues, persistent numbness or following a major fall.1 If back pain isn’t managed with effective treatment options, it can continue to progress, even leading to disability.
When is Back Pain Chronic?
It is essential to differentiate between acute and chronic back pain to determine the appropriate treatment plan. Acute back pain is usually caused by an injury or trauma to the back and lasts for a short period, usually less than six weeks. Acute back pain typically resolves on its own or with basic treatments such as rest, ice and over-the-counter pain medications such as Advil Dual Action Back Pain.
Chronic back pain, on the other hand, lasts for more than 12 weeks and can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. Chronic back pain requires proper management and treatment to relieve pain and improve mobility. It can come and go, but will return within that time period, causing not only pain but frustration.
Chronic Back Pain Relief
Chronic back pain relief is possible, and there are several ways to manage the condition. Here are some tips to find relief from chronic back pain:
- Physical therapy: a custom movement regimen may include retraining your posture, flexibility exercises and core strengthening.2
- Exercise regularly: low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking and yoga can help reduce back pain.
- Apply heat or cold: applying heat or cold to the affected area can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Improve posture: maintaining proper posture can help prevent back pain and reduce strain on the spine.
- Medications: some over-the-counter and prescription pain relievers may help alleviate chronic back pain.
- Massage therapy: regular sessions with a trained massage therapist can help relieve muscle tension and reduce pain.
- Acupuncture: this is an alternative therapy that can help reduce chronic back pain by stimulating the release of endorphins.3
It is important to note that chronic back pain relief may take time and require a combination of treatments. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment plan.
The Bottom Line
Chronic back pain is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The causes of chronic back pain can vary, but the good news is that relief is possible with proper management and treatment. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for chronic back pain.
Source Citations:
- Back Pain. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20369906. Accessed 3/21/2023.
- 7 Ways to Treat Chronic Back Pain Without Surgery. Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/back-pain/7-ways-to-treat-chronic-back-pain-without-surgery. Accessed 3/21/2023.
- Relieving Pain with Acupuncture. Harvard Health. https://www.health.harvard.edu/healthbeat/relieving-pain-with-acupuncture. Accessed 3/21/2023.
By clicking the link(s) above, you will be taken to an external website that is independently operated and not managed by Haleon. Haleon assumes no responsibility for the content on the website. If you do not wish to leave this website, do not click on the links above.