Cold, Flu or Sinus
Whether your symptoms include congestion, sneezing, sinus pressure, runny nose, fever or pain, Advil products can help. Discover which remedy is right for you.

Advil Multi-Symptom Cold & Flu
A unique triple-action formula relieves your worst cold & flu symptoms.
ANCHOR HERE
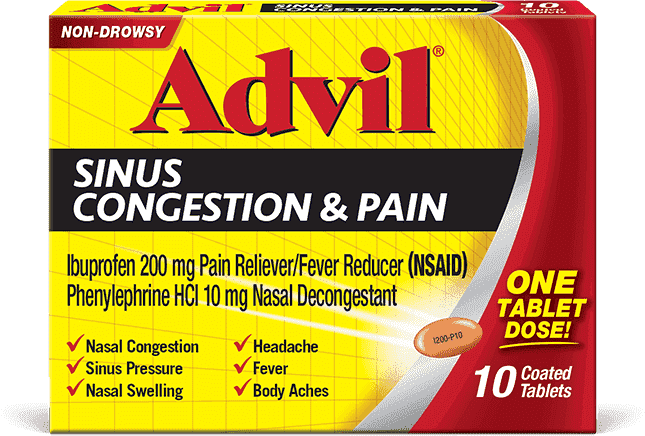
Advil Sinus Congestion & Pain
Relieve sinus pressure, nasal swelling, congestion and headaches.
ANCHOR HERE
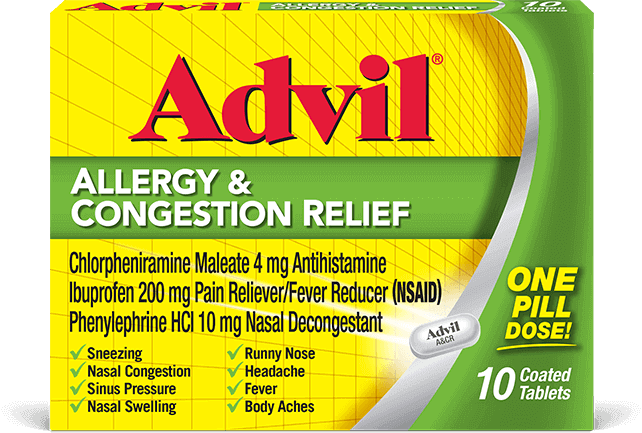
Advil Allergy Congestion & Relief
Relieves sinus pressure, nasal swelling, congestion, sneezing, runny nose and headache.
ANCHOR HERE

Advil Cold & Sinus
Reduce the swelling caused by nasal inflammation to breathe easier. Ask for it behind the pharmacy counter.
ANCHOR HERE
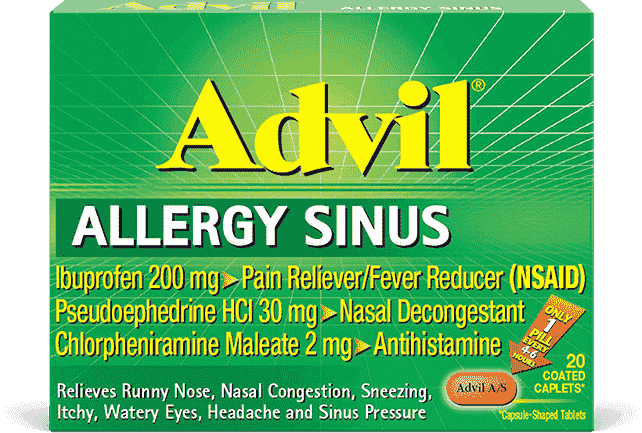
Advil Allergy Sinus
Allergy relief plus Advil relief, so you can stop allergies that hurt. Ask for it behind the pharmacy counter.
ANCHOR HERE
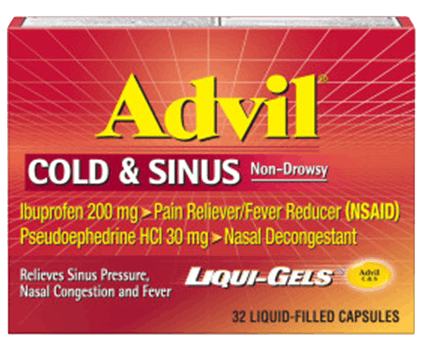
Advil Cold & Sinus Liqui Gels
Pain medicine with pseudoephedrine helps relieve nasal congestion and sinus pressure related to the common cold.
ANCHOR HERE
Compare Advil Products

Count 300
Form Tablets
Key feature Easy to swallow
Ingredient Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 tablet every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 200
Form Capsules
Key feature Small and easy to swallow
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
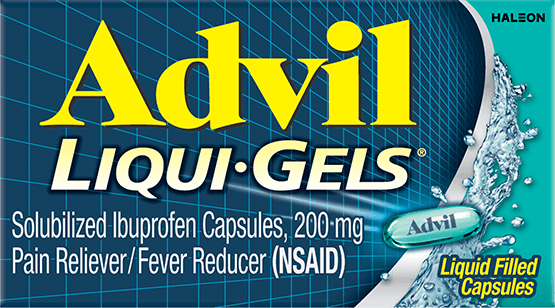
Count 160
Form Capsules
Key feature Fast-acting
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 200
Form Tablets
Key feature Easy open cap
Ingredient Ibuprofen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 tablet every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 144ct
Form Caplet
Key feature Target Back Pain
Ingredient Ibuprofen + Acetaminophen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 8h
Dosage 2 caplets every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 caplets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
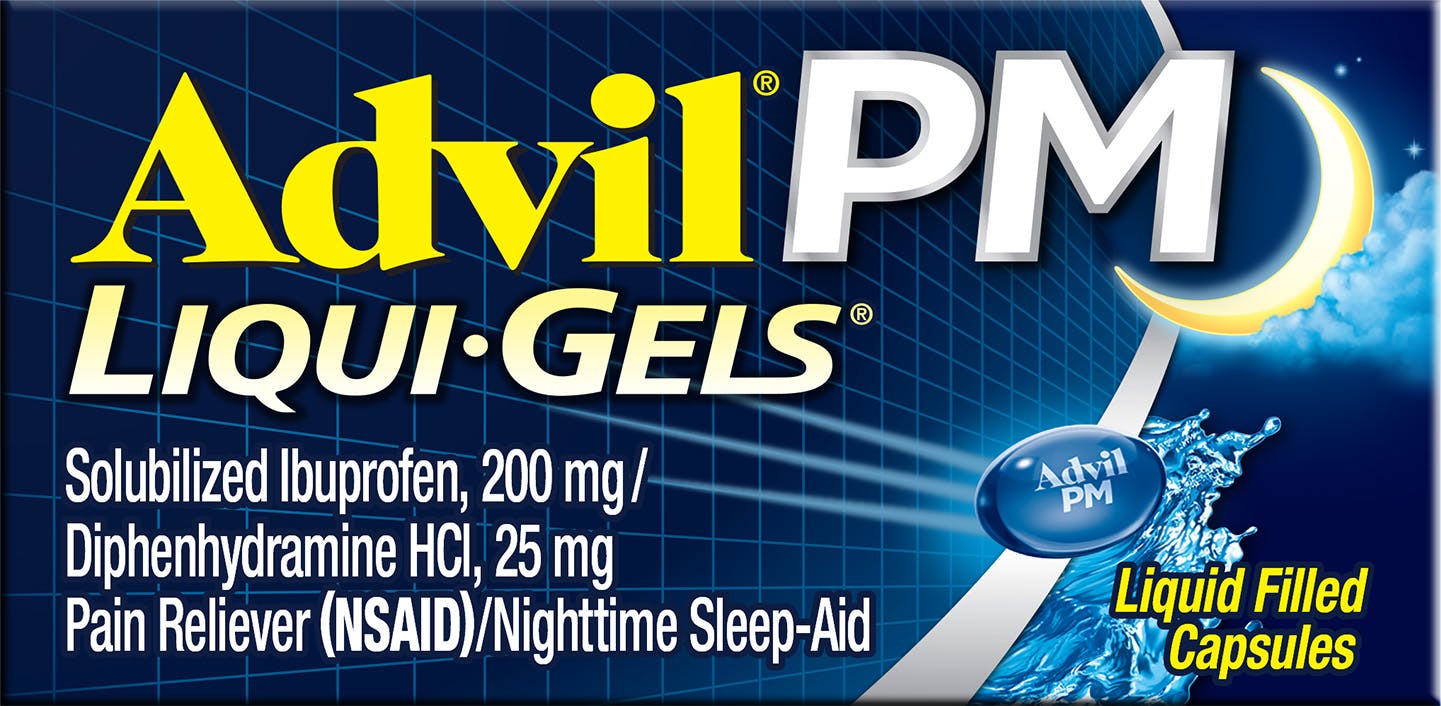
Count 80
Form Capsules
Key featurePain relief & 8 hours of sleep
Ingredient Solubilized Ibuprofen / Diphenhydramine
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Durationprovides pain relief and up to 8 hours of sleep
Dosage Take 2 capsules at bedtime. Do not take more than 2 capsules in 24h.

Count 160
Form Capsules
Key feature Fast-acting
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
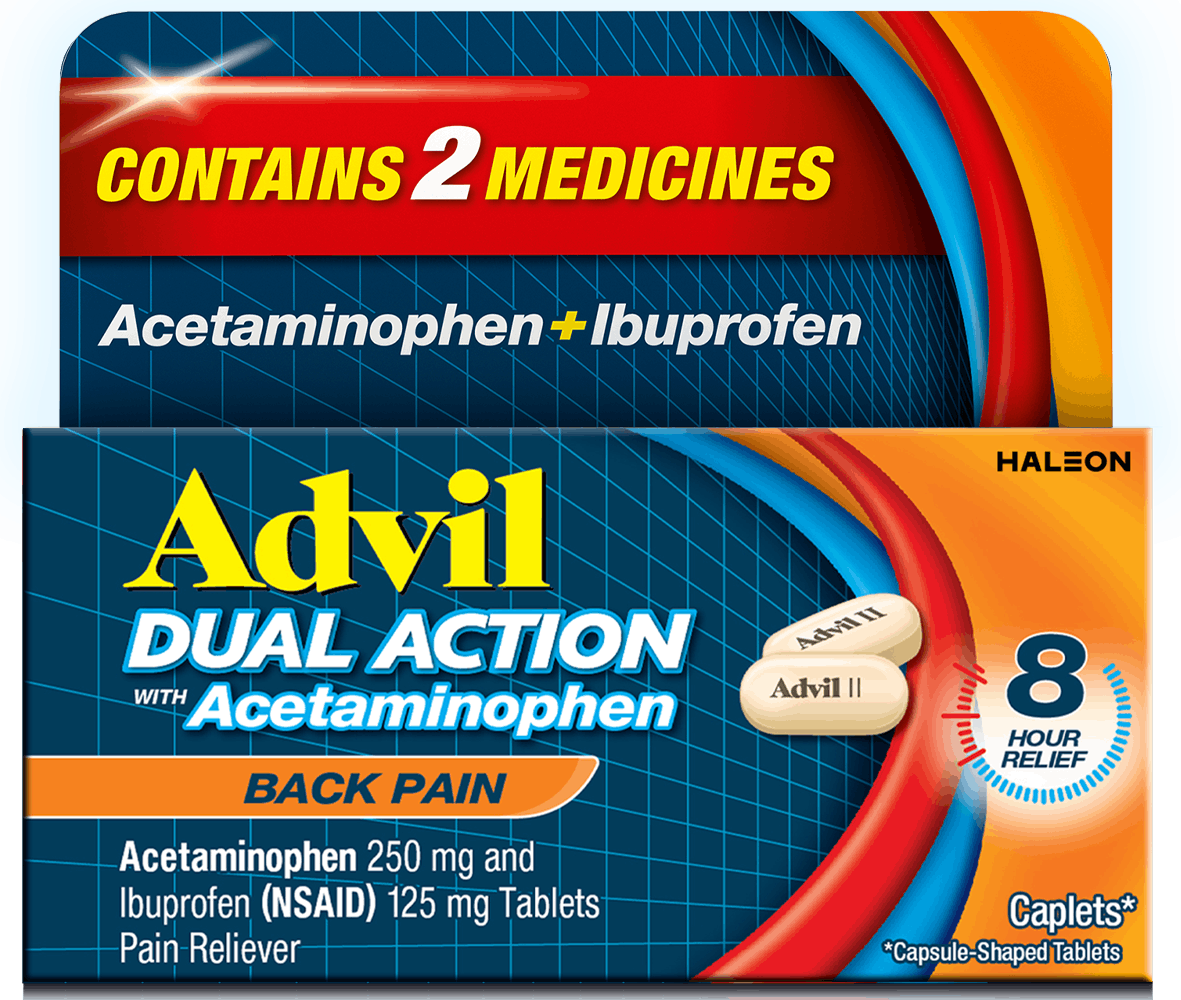
Count 144ct
Form Caplet
Key feature Targets Back Pain
Ingredient Ibuprofen + Acetaminophen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 8h
Dosage 2 caplets every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 caplets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
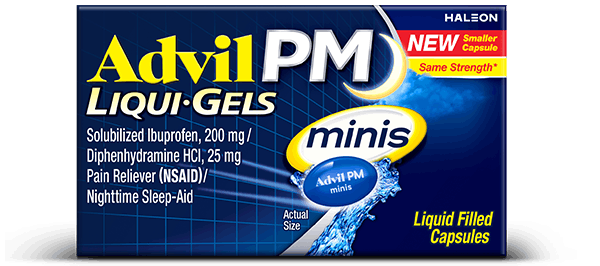
Count 80
Form Capsules
Key feature Pain relief & 8 hours of sleep
Ingredient Solubilized Ibuprofen / Diphenhydramine
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration provides pain relief and up to 8 hours of sleep
Dosage Take 2 capsules at bedtime. Do not take more than 2 capsules in 24h.

Count 200
Form Capsules
Key feature Small and easy to swallow
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 200
Form Tablets
Key feature Easy open cap
Ingredient Ibuprofen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 tablet every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 144ct
Form Caplet
Key feature Target Back Pain
Ingredient Ibuprofen + Acetaminophen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 8h
Dosage 2 caplets every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 caplets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 80
Form Capsules
Key featurePain relief & 8 hours of sleep
Ingredient Solubilized Ibuprofen / Diphenhydramine
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Durationprovides pain relief and up to 8 hours of sleep
Dosage Take 2 capsules at bedtime. Do not take more than 2 capsules in 24h.

Count 160
Form Capsules
Key feature Fast-acting
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 300
Form Tablets
Key feature Easy to swallow
Ingredient Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 tablet every 4 - 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 144ct
Form Caplet
Key feature Targets Back Pain
Ingredient Ibuprofen + Acetaminophen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 8h
Dosage 2 caplets every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 caplets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.

Count 80
Form Capsules
Key feature Pain relief & 8 hours of sleep
Ingredient Solubilized Ibuprofen / Diphenhydramine
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration provides pain relief and up to 8 hours of sleep
Dosage Take 2 capsules at bedtime. Do not take more than 2 capsules in 24h.